What is marketing automation and what are its benefits?
Automating processes is not a new topic, for years companies have been looking for ways to maximize their resources and marketing departments are no...
By Role
By Industry
By Target Customer
What We Offer
We drive business growth by improving operational efficiency through process optimization, smart automation, and cost control. Our approach boosts productivity, reduces expenses, and increases profitability with scalable, sustainable solutions
Customer Experience
We design memorable, customer-centered experiences that drive loyalty, enhance support, and optimize every stage of the journey. From maturity frameworks and experience maps to loyalty programs, service design, and feedback analysis, we help brands deeply connect with users and grow sustainably.
Marketing & Sales
We drive marketing and sales strategies that combine technology, creativity, and analytics to accelerate growth. From value proposition design and AI-driven automation to inbound, ABM, and sales enablement strategies, we help businesses attract, convert, and retain customers effectively and profitably.
Pricing & Revenue
We optimize pricing and revenue through data-driven strategies and integrated planning. From profitability modeling and margin analysis to demand management and sales forecasting, we help maximize financial performance and business competitiveness.
Digital Transformation
We accelerate digital transformation by aligning strategy, processes and technology. From operating model definition and intelligent automation to CRM implementation, artificial intelligence and digital channels, we help organizations adapt, scale and lead in changing and competitive environments.
Operational Efficiency
We enhance operational efficiency through process optimization, intelligent automation, and cost control. From cost reduction strategies and process redesign to RPA and value analysis, we help businesses boost productivity, agility, and sustainable profitability.
Customer Experience
Marketing & Sales
Pricing & Revenue
Digital Transformation
Operational Efficiency
Imagine repetitive and tedious tasks—those that consume hours of your team’s valuable time—being completed without human intervention and with impeccable accuracy.
These tasks aren’t just done faster; they’re done automatically, freeing your team to focus on what truly matters: crafting strategies, innovating, and delivering a memorable experience to your customers. This isn’t a fantasy—it’s the reality made possible by Robotic Process Automation, or RPA.
For many, the word “automation” can feel a bit intimidating. It brings to mind complex systems and technologies. But in reality, RPA is about digital tools that simplify daily work, streamline operations, and substantially improve business efficiency. In today’s increasingly competitive environment, why not harness its power to optimize and elevate your organization?
As more companies adopt RPA, common questions arise: What exactly is RPA? What is it used for, and how can it specifically benefit me? If you’ve ever wondered whether this technology is worth the investment, or how it might integrate into your existing processes, this article is for you. Here, we’ll explore not just the types of RPA available, but also its benefits, limitations, and the steps needed to implement it successfully in your organization.
The goal of this article is to provide clarity and answer your questions so you can make an informed decision about whether RPA is the right tool to elevate your company’s customer experience and operational efficiency. We’ll cover the following topics:
What is RPA?
Types of RPA
How does RPA work and what is it used for?
What processes can be automated with RPA?
When does RPA not make sense to implement?
Why should I implement RPA in my organization?
RPA Challenges
RPA Use Cases
What is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses specialized software to perform repetitive tasks automatically, without human involvement. Think of those routine office tasks that take time and effort—copying and pasting data, updating records, processing invoices. With RPA, these processes can be executed quickly and accurately by software “bots,” reducing manual workload and increasing operational efficiency. This technology is designed to mimic the actions a person would take on a computer, allowing automation of tasks ranging from data management to customer support across different applications and platforms.
RPA bots can be configured to interact with virtually any system or tool, without requiring changes to existing infrastructure. This makes RPA a versatile and easy-to-adopt solution for businesses of all sizes. Moreover, these bots can be programmed to follow defined rules and conditions, executing task sequences in a standardized, error-free manner. These virtual robots can handle a significant volume of work in less time and with consistent accuracy—translating into meaningful savings in both cost and time.
In essence, RPA doesn’t just reduce repetitive workloads—it empowers teams to focus on high-value activities such as strategy, decision-making, and innovation. In a landscape where efficiency and agility are critical, RPA stands out as a powerful tool to transform the way businesses operate, enhance the customer experience, and drive productivity at every level.
Types of RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has become a key tool for organizations aiming to increase operational efficiency and free their teams from repetitive, manual tasks. Through software "robots," RPA enables the execution of structured processes with speed and precision, significantly boosting productivity, reducing errors, and optimizing costs. However, not all RPA solutions are created equal—there are different types of automation that cater to varying business needs and levels of operational complexity.
Broadly speaking, RPA can be classified into three main categories: Attended RPA, Unattended RPA, and Hybrid RPA. Attended RPA works alongside human users, assisting with specific tasks within their workflow. In contrast, Unattended RPA operates independently, executing processes without human intervention—ideal for backend or batch operations. Finally, Hybrid RPA combines both approaches, offering a more flexible and scalable automation strategy. Understanding these categories is essential for designing an automation roadmap aligned with real business processes and team capabilities.
Rule-Based RPA: This form of structured automation follows predefined instructions to carry out specific tasks. It's ideal for clear and repetitive processes such as validating customer data, generating simple reports, or applying discounts based on fixed criteria. Rule-based RPA bots do not require analysis or learning—they simply execute tasks according to established rules, ensuring consistency and precision in standardized workflows.
Machine Learning-Based RPA: This type of automation leverages artificial intelligence to identify patterns and make decisions in real time, allowing for the automation of tasks that require a certain level of adaptability. Unlike rule-based RPA, machine learning-based bots can evolve and improve performance over time. This makes it possible to automate more complex processes such as data analysis, report generation, or pattern recognition across large volumes of information. It is especially useful in dynamic environments where context changes or where predictive insights are needed.

Unattended RPA (Unsupervised Automation)
Unattended RPA operates autonomously without requiring human intervention. These bots are typically deployed on servers and can run 24/7, enabling end-to-end process automation. Unattended automation is ideal for tasks that require continuous or scheduled execution, such as inventory management or account reconciliation. By working independently, unattended bots can significantly reduce processing times and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Attended RPA
Also known as “human-in-the-loop” automation, attended RPA works alongside employees to assist and accelerate specific tasks. These bots are triggered by user actions and operate on the user's desktop, executing in real time to address immediate needs. Attended automation is perfect for environments where users need digital assistance with repetitive tasks without fully replacing human input—such as in customer service or ad hoc administrative work.
Hybrid RPA
Hybrid RPA offers a comprehensive and flexible solution. This approach allows attended and unattended bots to work together, alternating tasks and sharing data to maximize efficiency in complex processes. Hybrid automation is ideal for companies that require automation at multiple levels, as it enables human intervention when necessary while maintaining background automation. This combination delivers greater adaptability and scalability for business processes that benefit from the best of both worlds.
How does RPA work and what Is it for?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) works by using software bots that replicate human actions in digital systems. These bots are programmed to interact with applications, databases, and other IT systems, mimicking tasks such as data entry, sending emails, or generating reports. By working directly through the user interface, bots can perform tasks quickly and accurately without requiring complex changes to existing systems—making RPA easy to implement within a company’s IT infrastructure.
The fundamental principles of RPA include the ability to execute predefined transactions, interact with multiple systems, and operate continuously. This contributes significantly to improving operational efficiency and reducing error margins. The RPA ecosystem includes key components: a design and development platform where workflows and bot tasks are configured, and a control and orchestration module that monitors performance in production. This governance layer ensures bots operate according to specifications and quality standards.
The primary goal of RPA is to shift the execution of repetitive, low-value tasks from humans to bots. This allows employees to focus on strategic initiatives and tasks that require creativity or decision-making, while bots handle structured, operational work. Additionally, RPA enables continuous operation—bots can run around the clock, optimizing time and resources.
One standout advantage of RPA is its ability to integrate with existing IT architecture without the need for deep or complex system modifications. Tools like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere enable flexible and adaptable automation, leading many companies to adopt RPA as a powerful solution to improve efficiency and drive productivity. With its ability to operate autonomously and error-free, RPA is a valuable technology for any business looking to reduce costs and enhance process quality.
RPA can automate a wide variety of repetitive, rule-based processes common across many business functions. This includes actions like copying and pasting structured data, moving files between systems, or executing if/then statements for decision-making. For instance, bots can open emails, classify attachments, or archive documents in specific folders—streamlining document management and improving the organization and efficiency of information workflows.
RPA also handles more complex tasks, such as extracting and classifying data from unstructured or low-quality documents, ensuring fast and accurate data collection. These datasets can then be redirected automatically to the appropriate platform, enhancing speed and reliability in data processing. By taking over operational tasks, RPA enables teams to focus on higher-value activities such as data analysis and improving customer experience.
RPA isn’t suitable for every scenario. It generally doesn’t add value when tasks are infrequent, highly variable, or involve many exceptions. Automating such processes would require constant adjustments, which can reduce efficiency and drive up costs. Processes that heavily rely on human judgment or that must adapt dynamically to changing contexts are also poor candidates, as bots lack the ability to interpret nuance or make flexible decisions.
Moreover, a poorly planned RPA implementation can cause more harm than good. For example, if workflows are not well defined, automation may create bottlenecks instead of resolving them. Similarly, replicating existing errors within automated tasks can amplify operational issues. If automation is misaligned with departmental goals, it can limit RPA's effectiveness and even hurt productivity by introducing inconsistencies.
For these reasons, it's essential to thoroughly assess company needs and goals before adopting RPA. A well-planned, tailored approach can make RPA a valuable asset—but without careful evaluation, it’s unlikely to deliver the expected results.
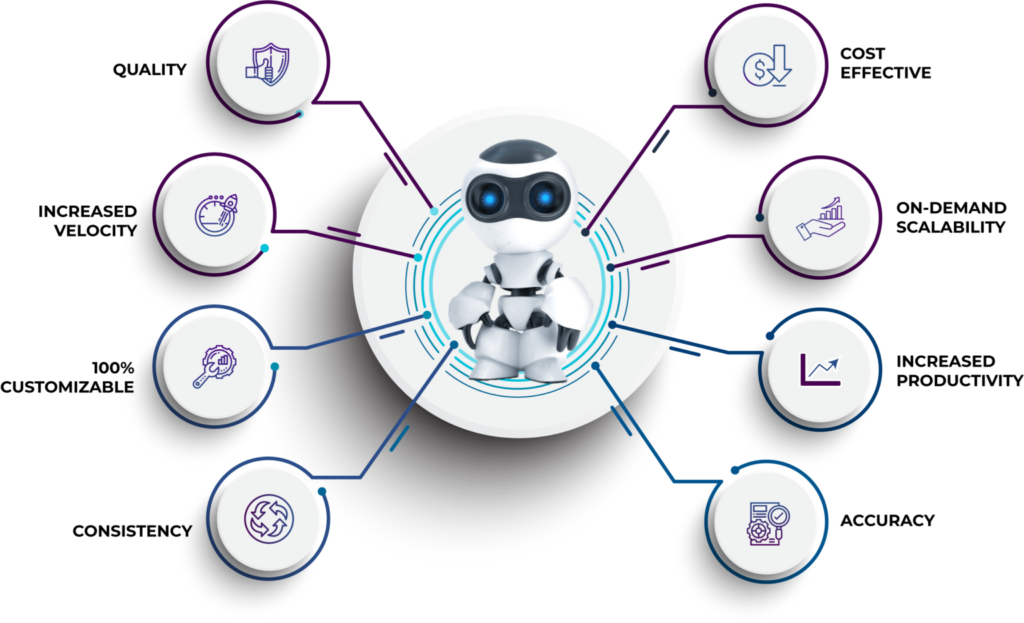
Why should i implement RPA technology in my company?
Implementing RPA technology in your company offers a number of key advantages that can transform the efficiency and performance of your operations. One of the main reasons to adopt RPA is that it ensures compliance with established procedures by automating tasks according to predefined standards, which reduces the possibility of human error and ensures that processes are carried out consistently. Additionally, RPA increases team productivity by freeing employees from repetitive, manual tasks, allowing them to focus on higher-value strategic activities that drive business growth.
Another significant benefit of RPA is process acceleration. By eliminating the need for human intervention at every step, bots can execute tasks much faster than employees, resulting in a noticeable improvement in operational efficiency. RPA also facilitates process auditing by providing a clear and detailed view of all automated activities, allowing for quick identification of areas for improvement, bottlenecks, and potential incidents. This, in turn, contributes to more efficient and optimized management of company resources.
In addition to improving efficiency, implementing RPA can significantly reduce error rates. Manual tasks, especially repetitive ones, are prone to human mistakes; however, robots follow predefined rules with great precision, virtually eliminating errors. This not only improves the quality of outcomes but also leads to significant cost savings. While RPA implementation requires an initial investment, it offers long-term savings by automating tasks that previously required human intervention. Lastly, RPA offers fast and simple scalability, allowing companies to adjust and expand bot capacity as needed, which is ideal for growing businesses requiring operational flexibility.
>> ALSO READ: Systematization and Automation: A Successful Digital Transformation <<
RPA Challenges
While Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers significant benefits in terms of efficiency, error reduction, and operational scalability, its implementation is not without challenges. Many organizations face obstacles that go beyond the technical, including cultural resistance, governance issues, and misaligned expectations. These challenges can hinder the expected impact of automation or even lead to team frustration if not addressed early with a clear and well-communicated strategy.
Key challenges include employee resistance to change, lack of standardized processes, limited scalability due to a lack of holistic vision, and overestimating what RPA can achieve without proper integration with other technologies like BPM, AI, or ERP systems. Moreover, managing the bot lifecycle—from development to maintenance—requires strong governance and collaboration between business and technology teams. Overcoming these challenges means viewing RPA not as an end in itself but as an enabler within a broader digital transformation roadmap.
Implementations
RPA implementation can be a fast and straightforward process, but this largely depends on the existing technological infrastructure and the tools with which the bots interact. For automation to be effective, it is essential to fully understand the processes to be automated and to have a robust infrastructure capable of handling increased workloads in terms of both performance and storage. If the infrastructure is not properly prepared, it may become a barrier to a smooth and scalable deployment of automation.
Resistance to change is a common challenge when implementing RPA within organizations. Employees often feel job insecurity, perceiving robots as a threat to their roles. To mitigate this resistance, effective communication about the benefits of automation is essential, emphasizing that bots are tools designed to complement, not replace, human work. Training employees to understand how RPA can help them become more productive and focus on higher-value tasks is key to overcoming this challenge.
Once implemented, RPA systems require ongoing maintenance and updates to stay aligned with changes in business processes and the IT systems they interact with. If bots are not updated regularly, they risk causing operational errors or falling out of sync with evolving business needs. Therefore, it is essential to have a proper maintenance and error management plan in place to adapt the bots as business processes evolve, ensuring continued efficiency.
RPA implementation also brings challenges related to ethics and security. One of the most critical aspects is ensuring that bots do not perform tasks that could infringe on data privacy or violate regulatory standards. In addition, best practices must be applied in protecting the information managed by bots to avoid data leaks or losses. Companies must therefore enforce strict security policies to protect both data and legal compliance within their automated processes.
Despite its evident benefits, some companies remain skeptical about the effectiveness of RPA. This skepticism often arises in organizations with no prior experience with the technology or a limited understanding of its capabilities. Concerns typically revolve around whether bots can execute tasks flawlessly or adapt to changing situations. To overcome this, it's essential to showcase success stories, set clear expectations, and conduct pilot programs to measure the effectiveness of RPA before full-scale implementation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has evolved from being a tactical solution for repetitive tasks to a strategic tool for transforming operational efficiency across multiple industries. Its ability to replicate human actions on digital interfaces allows automation of everything from simple tasks like data entry to more complex workflows involving multiple systems and business rules. This has opened a wide range of possibilities in areas such as finance, human resources, logistics, customer service, and IT—domains where manual processes are time-consuming and prone to bottlenecks.
Common use cases include invoice reconciliation, report generation, purchase order management, employee onboarding, claims processing, and system monitoring. Each of these scenarios shares a key need: freeing up human teams from operational tasks so they can focus on higher-value activities. Moreover, RPA is highly adaptable, allowing for automation designs that respect the unique characteristics of each business and integrate with existing systems without requiring costly infrastructure changes. Together, these use cases demonstrate that RPA not only reduces costs but also improves accuracy, speed, and both internal and external customer experience.
Finance and accounting
The finance and accounting sector constantly faces the need to manage large volumes of data and perform time-consuming, repetitive tasks. RPA has proven to be an effective solution for optimizing operations. Common use cases include automating general ledger entries, managing accounts payable and receivable, and handling financial reports and statements. These processes, traditionally requiring significant manual input, are significantly accelerated through RPA, enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
In HR, RPA provides substantial benefits, especially in automating bureaucratic and repetitive processes that depersonalize employee interactions. Bots can handle tasks such as collecting and screening resumes, scheduling interviews, and managing administrative onboarding tasks. They can also automate payroll management and ensure regulatory compliance. As a result, HR teams can focus on more strategic, value-adding tasks, enhancing the experience of both employees and candidates.
RPA also positively impacts customer service operations. Through the integration of chatbots and other automated systems, companies can provide fast and effective responses to common inquiries, improving user experience. Additionally, bots can gather relevant customer information and pass it to human agents, optimizing response time and personalizing support. This synergy between bots and humans not only speeds up problem resolution but also increases customer satisfaction and loyalty.
RPA has become an essential tool in IT and data management Digital Transformation. Automating tasks like user account creation, system configuration, or backup generation frees IT teams from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on more critical projects. Furthermore, RPA plays a crucial role in managing and analyzing large volumes of data, ensuring accuracy and consistency. By automating data collection, processing, and analysis, companies can access more accurate insights and make better-informed real-time decisions.

Automating processes is not a new topic, for years companies have been looking for ways to maximize their resources and marketing departments are no...

Business Process Management (BPM) is a crucial methodology for any organization aiming to optimize operations and remain competitive in an...

Today’s business environment demands that organizations adopt fast and efficient technological solutions to remain competitive.